What Are Carbon Credits?
Carbon credits are a form of tradable permit representing the right to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases. Each carbon credit typically allows the holder to emit one ton of CO2 or its equivalent in other greenhouse gases.
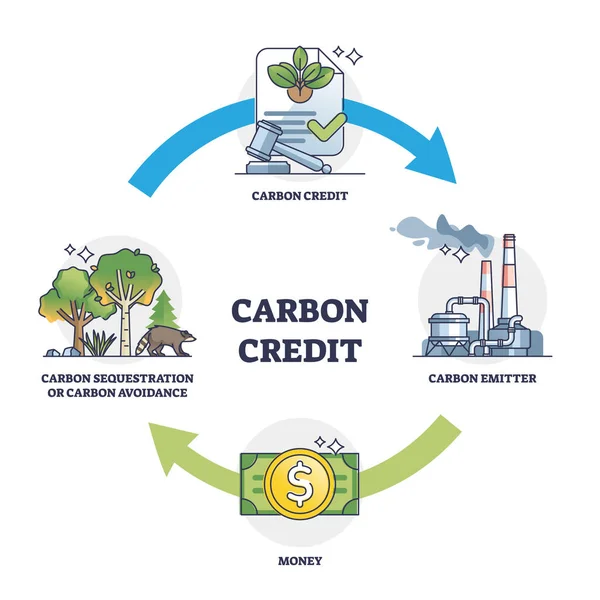
Purpose of Carbon Credits
The primary purpose of carbon credits is to reduce the overall emissions of greenhouse gases. By putting a price on carbon emissions, carbon credits incentivize companies and individuals to invest in cleaner, more sustainable practices. The system is designed to mitigate climate change by encouraging reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
How Do Carbon Credits Work?
- Cap-and-Trade System:
- Cap: A limit is set on the total amount of greenhouse gases that can be emitted by all participating entities.
- Trade: Companies or organizations that need to exceed their emission allowances can buy credits from those who have excess credits. This creates a market for carbon credits and provides a financial incentive for reducing emissions.
- Offsetting:
- Organizations can invest in projects that reduce emissions elsewhere, such as reforestation or renewable energy projects. The reductions achieved by these projects can be quantified and converted into carbon credits.
Types of Carbon Credits
- Compliance Carbon Credits: Used by companies and countries to comply with regulatory limits on greenhouse gas emissions. These credits are often part of a cap-and-trade system.
- Voluntary Carbon Credits: Purchased by individuals, companies, or organizations voluntarily to offset their carbon footprint. These are often used as part of corporate social responsibility initiatives.
Key Components of Carbon Credit Markets
- Regulation: Governments or international bodies set emission limits and regulations.
- Certification: Independent third parties verify that the emission reductions are real, measurable, and permanent. Certification ensures the credibility of carbon credits.
- Marketplaces: Platforms where carbon credits are traded. These can be government-run or private exchanges.
Benefits of Carbon Credits
- Environmental Impact: By limiting and reducing greenhouse gas emissions, carbon credits help mitigate climate change.
- Economic Efficiency: Carbon credits create a financial incentive for companies to innovate and reduce emissions cost-effectively.
- Sustainable Development: Projects funded by carbon credits often provide additional benefits such as improved air quality, job creation, and conservation of biodiversity.
Challenges and Criticisms
- Verification and Fraud: Ensuring the integrity and authenticity of carbon credits can be challenging. There have been instances of fraud and double-counting.
- Market Volatility: The price of carbon credits can be highly volatile, making it difficult for companies to plan long-term investments.
- Equity Issues: There are concerns that carbon credit systems may disproportionately benefit wealthier countries and companies, leaving developing countries and smaller entities at a disadvantage.
The Future of Carbon Credits
- Enhanced Regulation and Standards: Efforts are being made to improve the transparency, reliability, and effectiveness of carbon credit systems.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in technology can enhance the monitoring and verification of emission reductions.
- Global Cooperation: Greater international collaboration can help harmonize carbon credit systems and ensure broader participation and impact.
Conclusion
Carbon credits are a crucial tool in the fight against climate change, offering a market-based approach to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Understanding how they work, their benefits, and the challenges they face is essential for leveraging their full potential in creating a more sustainable future.



Leave a Reply