Introduction
As the world grapples with the escalating effects of climate change, the importance of carbon credits as a tool for mitigating greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions has grown substantially. In India, the development and adoption of innovative technologies have played a crucial role in enhancing the generation of carbon credits. These technologies not only help in reducing emissions but also contribute to sustainable development by promoting cleaner and more efficient energy, agriculture, and industrial practices. This essay explores the various technologies and innovations driving carbon credit generation in India, their impact, challenges, and future potential.
The Role of Technology in Carbon Credit Generation
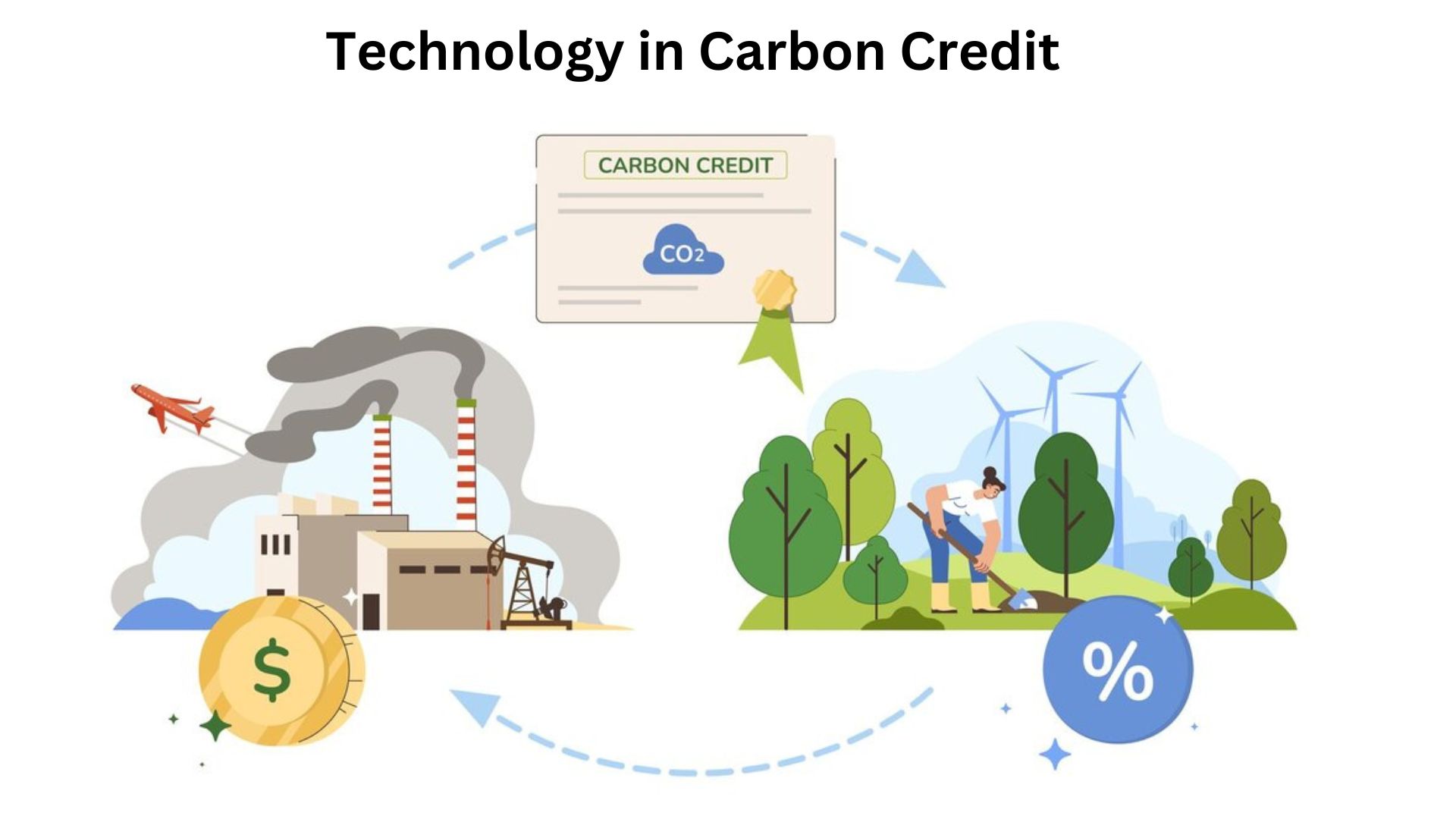
Carbon credits are generated through activities that reduce, avoid, or sequester GHG emissions. The effectiveness and efficiency of these activities are often determined by the technologies employed. In India, a country with diverse environmental challenges and opportunities, the integration of technology has been key to scaling up carbon credit generation across various sectors.
Innovations in renewable energy, waste management, agriculture, and forestry have significantly contributed to the country’s ability to generate carbon credits. These technologies not only enable more accurate measurement and verification of emission reductions but also enhance the sustainability and profitability of the projects involved.
Key Technologies in Carbon Credit Generation
- Renewable Energy Technologies:
- Solar and Wind Power: Solar and wind energy are the backbone of India’s renewable energy sector, contributing significantly to carbon credit generation. Technological advancements in photovoltaic (PV) cells, wind turbines, and energy storage have made renewable energy more reliable and cost-effective. These technologies help displace fossil fuel-based power generation, leading to substantial reductions in CO2 emissions and the generation of carbon credits.
- Bioenergy: Biomass and biogas technologies utilize organic waste to produce energy, reducing methane emissions from waste decomposition. Innovations in bioenergy, such as advanced anaerobic digestion systems and efficient biomass gasification, have enhanced the potential for carbon credit generation in rural and agricultural areas.
- Waste Management and Circular Economy Technologies:
- Waste-to-Energy: Waste-to-energy technologies convert municipal solid waste into electricity or heat, thereby reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills and lowering methane emissions. India has seen the development of advanced incineration, gasification, and pyrolysis technologies that enhance the efficiency of waste-to-energy projects, making them viable sources of carbon credits.
- Recycling and Material Recovery: Innovations in recycling technologies, including advanced sorting and processing systems, help reduce the carbon footprint of materials by lowering the demand for virgin resources. These technologies contribute to carbon credit generation by reducing emissions associated with raw material extraction, processing, and disposal.
- Agricultural and Forestry Technologies:
- Precision Agriculture: Precision agriculture technologies, such as GPS-guided equipment, soil sensors, and drones, enable farmers to optimize resource use and reduce emissions. By minimizing the application of fertilizers and pesticides, these technologies reduce nitrous oxide emissions, a potent GHG, and enhance carbon sequestration in soils, generating carbon credits.
- Agroforestry and Reforestation: Innovations in agroforestry and reforestation practices, including the use of high-yield, fast-growing tree species and advanced planting techniques, have improved the carbon sequestration potential of forestry projects in India. These technologies support the generation of carbon credits by increasing the biomass and carbon storage capacity of forests.
- Industrial and Energy Efficiency Technologies:
- Energy Efficiency in Industry: Advanced technologies for energy efficiency, such as high-efficiency boilers, heat recovery systems, and variable speed drives, have been widely adopted in India’s industrial sector. These technologies reduce energy consumption and GHG emissions, generating carbon credits through improved industrial performance.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): Although still in the early stages of development in India, CCS technology has the potential to capture and store CO2 emissions from industrial processes and power plants. This technology could play a significant role in generating carbon credits, particularly as India seeks to decarbonize its industrial sector.
Innovations in Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV)
The credibility of carbon credits hinges on robust Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) systems that ensure accurate measurement of emission reductions. In India, innovations in MRV technologies have been instrumental in enhancing the transparency and reliability of carbon credit generation:
- Remote Sensing and Satellite Imagery: Remote sensing technologies, including satellite imagery and drones, are increasingly used to monitor land-use changes, forest cover, and agricultural practices. These technologies provide real-time data that improves the accuracy of carbon sequestration measurements and reduces the risk of double-counting or overestimating emission reductions.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology offers a transparent and tamper-proof method for tracking carbon credits from generation to sale. By creating a decentralized ledger, blockchain ensures that each carbon credit is uniquely identified and verified, reducing the risk of fraud and enhancing market trust.
- Big Data and AI: Big data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) are used to analyze vast amounts of environmental data, predict emission trends, and optimize carbon credit projects. These technologies enable more precise MRV processes, ensuring that carbon credits accurately reflect the emission reductions achieved.
Challenges in Technology Adoption
Despite the progress, several challenges hinder the widespread adoption of these technologies in carbon credit generation in India:
- High Initial Costs: Many of the advanced technologies required for carbon credit projects, such as solar PV systems or precision agriculture equipment, have high upfront costs. This can be a barrier, especially for small-scale projects or those in economically disadvantaged areas.
- Technical Expertise: Implementing and maintaining these technologies requires specialized knowledge and skills. In many parts of India, there is a lack of technical expertise, which can limit the effectiveness of carbon credit projects and their ability to generate verifiable credits.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory environment for carbon credits in India is still evolving, with occasional ambiguities in policies related to carbon markets, land use, and energy projects. This uncertainty can deter investment in new technologies and projects.
- Market Volatility: The price of carbon credits can be volatile, influenced by global market trends and policy changes. This volatility can make it difficult for project developers to predict returns on investment, which in turn affects the adoption of new technologies.
Future Prospects and Opportunities
The future of carbon credit generation in India is closely tied to the continued development and adoption of innovative technologies. Several trends and opportunities could drive growth in this sector:
- Government Support: Continued government support through policies, subsidies, and incentives will be crucial in promoting the adoption of carbon credit-generating technologies. Initiatives such as the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) and the National Solar Mission provide a strong policy framework for expanding the use of clean technologies.
- International Collaboration: Collaboration with international organizations, technology providers, and carbon markets can help India access the latest technologies and expertise. Partnerships with countries leading in carbon capture, renewable energy, and MRV innovations can accelerate the adoption of these technologies in India.
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing advancements in technologies such as AI, blockchain, and energy storage will continue to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of carbon credit projects. As these technologies become more accessible and affordable, they will play a larger role in India’s carbon market.
- Private Sector Engagement: Increasing interest from the private sector in sustainability and carbon neutrality will drive demand for carbon credits and the technologies that generate them. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives and voluntary commitments to reduce carbon footprints are likely to boost investment in carbon credit-generating technologies.
- Integration with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Aligning carbon credit projects with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) can attract broader support and funding. Technologies that contribute to multiple SDGs, such as renewable energy and clean water, will have a competitive edge in both carbon markets and development finance.
Conclusion
Technologies and innovations are at the heart of India’s efforts to generate carbon credits and combat climate change. From renewable energy and waste management to precision agriculture and blockchain, a wide range of technologies is driving the country’s carbon credit market forward. While challenges remain, the future is promising, with continued advancements, government support, and private sector engagement expected to play a pivotal role. As India navigates its path towards a low-carbon future, the adoption of cutting-edge technologies will be key to unlocking the full potential of carbon credits and achieving sustainable development goals.


Leave a Reply