
Carbon reduction projects are diverse initiatives aimed at lowering greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, mitigating climate change, and fostering a more sustainable future. These projects vary in scale, scope, and approach, often focusing on different sectors such as energy, agriculture, transportation, and waste management. Below is a comprehensive overview of the key types of carbon reduction projects:
1. Renewable Energy Projects
These projects focus on shifting energy production from fossil fuels to clean, renewable sources, thereby reducing emissions associated with electricity and heat generation.
- Solar Power: Installing solar panels on homes, businesses, or solar farms to harness energy from the sun.
- Wind Power: Developing onshore or offshore wind farms to capture energy from the wind.
- Hydropower: Using water flow in dams or rivers to generate electricity.
- Geothermal Energy: Utilizing heat from within the Earth to generate power.
- Biomass Energy: Burning organic material (wood, agricultural waste) in a way that captures energy without releasing excess carbon.
2. Energy Efficiency Projects
Energy efficiency initiatives aim to reduce the amount of energy consumed by improving the efficiency of systems, buildings, or devices, thus cutting emissions.
- Building Retrofitting: Upgrading insulation, windows, and heating/cooling systems in buildings to reduce energy consumption.
- Efficient Appliances and Lighting: Promoting the use of energy-efficient appliances, such as LED lighting or energy star-rated devices.
- Industrial Efficiency: Optimizing industrial processes, reducing energy loss in manufacturing, and adopting technologies such as Combined Heat and Power (CHP) systems.
3. Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS)
These projects focus on capturing CO2 emissions from industrial processes or power plants, storing them underground, or using the captured CO2 in other processes.
- Direct Air Capture (DAC): Capturing CO2 directly from the atmosphere for storage or reuse.
- Industrial Carbon Capture: Capturing emissions from factories or energy plants before they enter the atmosphere.
- CO2 Utilization: Using captured carbon to create products such as building materials, fuels, or chemicals.
4. Afforestation, Reforestation, and Forest Management
Forestry projects aim to increase the absorption of CO2 through the planting and management of trees and forests.
- Afforestation: Planting trees in areas where forests did not previously exist.
- Reforestation: Restoring forests that have been cut down or degraded.
- Forest Conservation: Protecting existing forests from deforestation to maintain their role as carbon sinks.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees into agricultural systems to enhance carbon sequestration while maintaining food production.
5. Agricultural and Land Use Projects
Agriculture and land-use projects focus on reducing emissions from farming and land management practices, which are major sources of methane and nitrous oxide.
- Soil Carbon Sequestration: Enhancing soil’s ability to absorb and store carbon through practices like cover cropping, reduced tillage, and crop rotation.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Promoting organic farming, precision agriculture, and low-emission livestock practices to reduce methane and nitrous oxide emissions.
- Wetland and Peatland Restoration: Protecting and restoring wetlands, peatlands, and mangroves, which store large amounts of carbon.
6. Waste Management and Circular Economy
Waste management projects focus on reducing emissions by managing waste more efficiently and minimizing the generation of waste.
- Landfill Gas Capture: Capturing methane emissions from landfills and using it for energy production.
- Waste-to-Energy: Converting waste materials into electricity or heat instead of sending them to landfills.
- Recycling and Composting: Reducing waste generation by recycling materials and composting organic waste, which reduces methane emissions.
7. Sustainable Transportation Projects
Transportation projects aim to lower emissions by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting cleaner modes of transport.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Supporting the adoption of electric vehicles to replace gasoline and diesel-powered cars.
- Public Transit Expansion: Developing efficient and low-emission public transportation systems such as buses, subways, and rail.
- Non-Motorized Transport: Promoting walking, cycling, and bike-sharing programs to reduce emissions from cars.
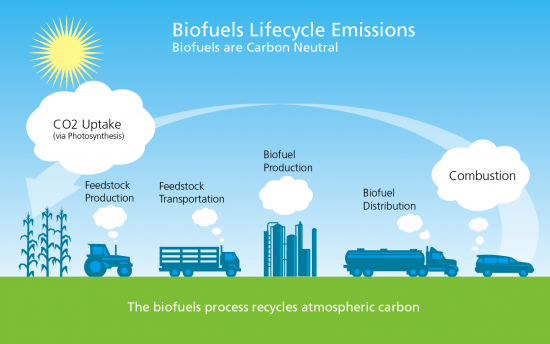
- Biofuels: Encouraging the use of biofuels in aviation, shipping, and road transport.
8. Carbon Offsetting Projects
Carbon offsetting involves investing in projects that remove or reduce CO2 to compensate for emissions that occur elsewhere.
- Renewable Energy Offsets: Supporting renewable energy projects through carbon credits.
- Forestry Offsets: Investing in afforestation or reforestation to offset emissions.
- Community Projects: Supporting projects in developing countries that reduce emissions through clean cooking stoves, renewable energy access, or improved water supply.
9. Behavioral Change and Education Programs
Some carbon reduction projects focus on fostering behavioral changes and increasing awareness of low-carbon lifestyles.
- Awareness Campaigns: Educating individuals and businesses on how to reduce their carbon footprint through energy savings, waste reduction, and sustainable consumption.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction Tools: Providing tools and apps to track and manage individual or organizational carbon footprints.
- Green Certification Programs: Encouraging businesses to adopt sustainability practices by achieving green certifications (e.g., LEED, B Corp).
10. Urban Planning and Smart Cities
Urban development projects that promote sustainable city planning and smart infrastructure can lead to significant reductions in emissions.
- Smart Grids: Using advanced technologies to optimize energy distribution and consumption in urban areas.
- Green Building Design: Incorporating energy-efficient design, renewable energy, and sustainable materials into urban development.
- Low-Carbon Communities: Developing neighborhoods that prioritize renewable energy, green spaces, and efficient transportation networks.
Conclusion
Carbon reduction projects span various sectors and strategies, from technological innovation to nature-based solutions and behavioral changes. The key to their success lies in global collaboration, strong policy frameworks, and the integration of multiple approaches to address the complex challenges posed by climate change.

Leave a Reply